Article
AvosLocker Adds Veritas Vulnerabilities to its Initial Access Arsenal
Ransomware group is targeting popular data recovery software, despite patch being available since March 2021
At-Bay’s Cyber Research Team has confirmed that AvosLocker, a well-known ransomware syndicate, is using several vulnerabilities in popular data backup and recovery software as a means to launch ransomware attacks.
Backup Exec is a backup and recovery software solution designed for businesses of all sizes. Owned and managed by Veritas, it provides a comprehensive backup and recovery system for Windows and Linux-based servers, as well as for virtual machines and individual workstations.
In March 2021, Veritas released a fix for three vulnerabilities that could allow for remote code execution (RCE). The vulnerabilities, identified as CVE-2021-27876, CVE-2021-27877 and CVE-2021-27878, existed due to a flaw in the SHA authentication scheme used by Backup Exec.
While fixes have been available, Ransomware-as-a-service (RaaS) groups have found organizations using unpatched versions. Attackers then use the unpatched software as an initial access vector, giving them internal access where they can distribute malware that will encrypt an organization’s entire IT system.
The Cyber Research team at At-Bay observed AvosLocker exploit Backup Exec vulnerabilities to launch a ransomware attack beginning in January 2023. The group is not the first RaaS gang to use Backup Exec as an initial access vector. In October 2022, cyber security firm Mandiant revealed that an affiliate of the ALPHV/BlackCat RaaS group was targeting publicly exposed Backup Exec installations to launch ransomware attacks.
Organizations can find more information on Veritas Backup Exec and AvosLocker below.
What Is The AvosLocker Ransomware Group?
AvosLocker is a ransomware-as-a-service (RaaS) group that first emerged in July 2021 and has since released multiple variants. Attackers using this malware encrypt IT systems, exfiltrate organizational data, and threaten to publicly leak their data unless a ransom is paid.
The group and its affiliates are known to target IT management or maintenance software, such as Zoho ManageEngine ServiceDesk Plus and Veeam Backup and Replication Software, in order to gain initial access. Attackers then deploy webshells and AnyDesk for lateral movement in an organization’s network.
The group has targeted a variety of sectors in India, Canada, and the United States.
Which Veritas Backup Exec Are Impacted?
| Product | Affected versions | Fixed versions |
| Backup Exec | 16.x | 21.2 and later |
| Backup Exec | 20.x | 21.2 and later |
| Backup Exec | 21.x | 21.2 and later |
| Backup Exec Agent | All |
How are The Vulnerabilities Being Exploited?
Attackers are exploiting these vulnerabilities by chaining together all three of the listed CVEs.
Veritas Backup Exec Agent supports multiple authentication schemes, including SHA authentication.1 An attacker could remotely exploit the SHA authentication scheme to gain unauthorized access to the Backup Exec Agent and execute arbitrary OS commands on the host with system/root user privileges, depending on the platform. This authentication scheme was removed from new versions of Backup Exec, but hadn’t yet been disabled in the impacted versions.
Exploiting the vulnerabilities can be done in a few steps:
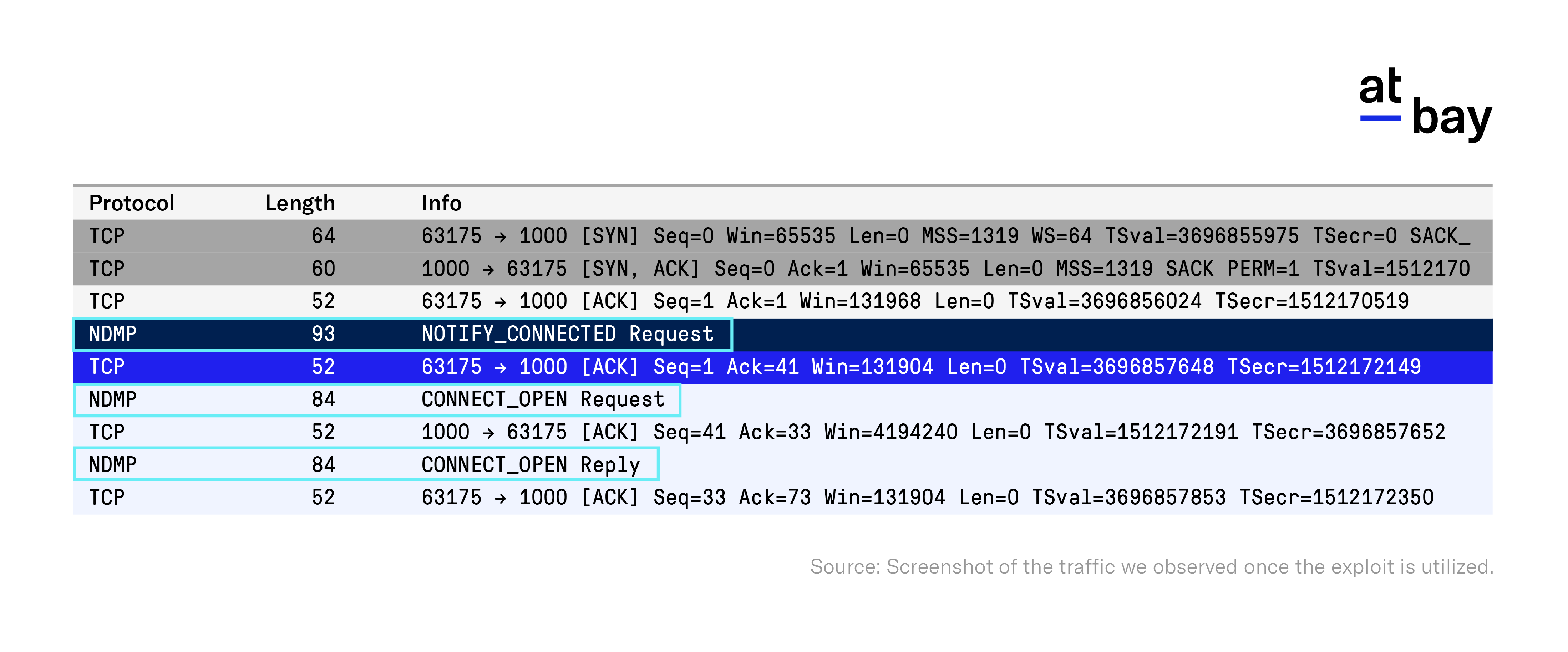
1. An attacker attempts to connect to the Veritas Backup Exec Agent using the NDMP.2 When the attacker receives a NOTIFY_CONNECT packet from the Backup Exec NDMP server. Then an attacker sends a CONNECT_OPEN request to the server and gets a CONNECT_OPEN reply packet. With the right status code, an attacker will know they have a connection.
2. An attacker then sends the Backup Exec NDMP server a config_get_server_info request to check what types of authentication are supported by the server.
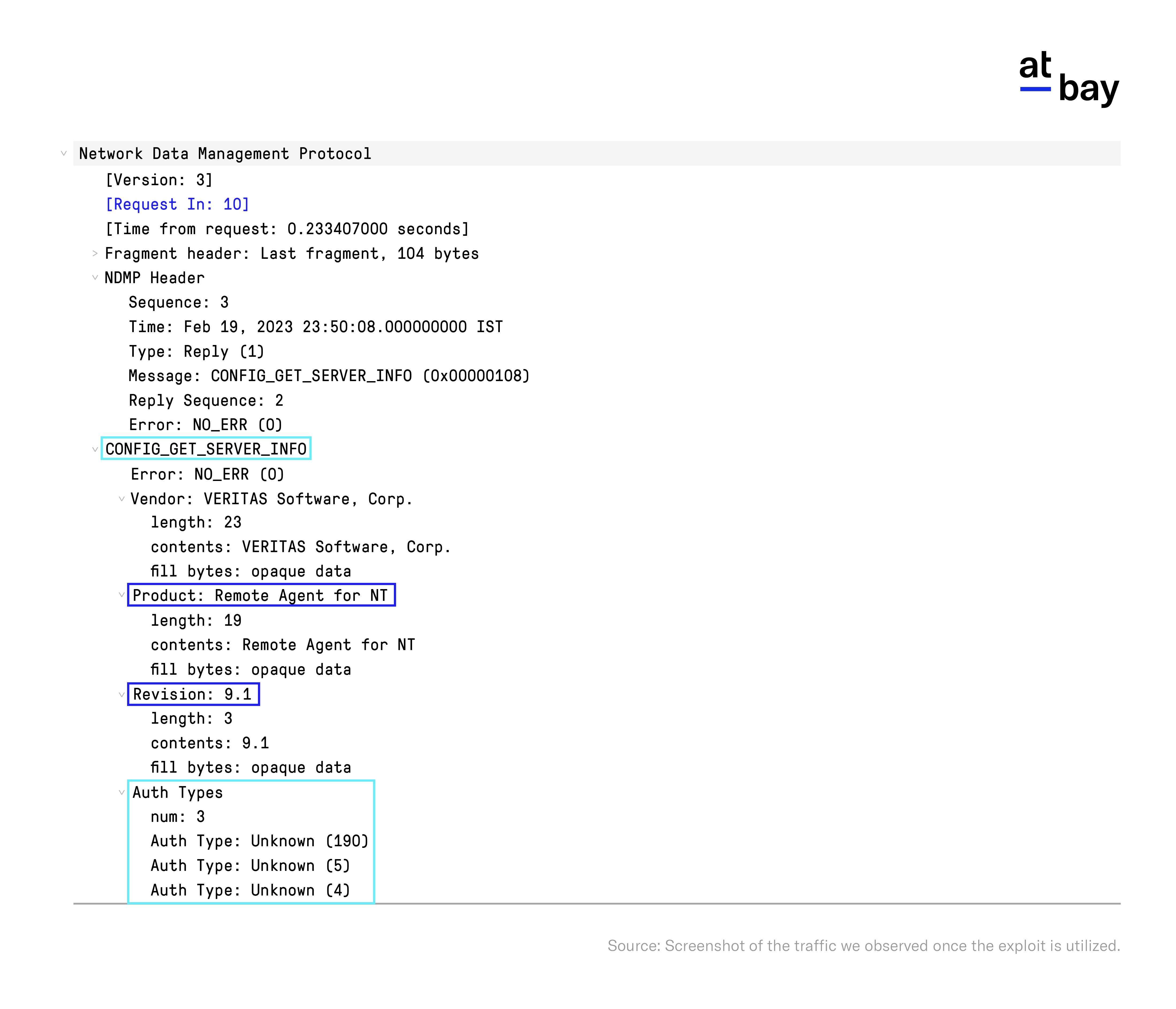
3. An attacker then checks if the server has SHA authentication enabled – the content of the packet should include Auth Type: Unknown (5). The attacker authenticates their connection.

4. The attacker uploads a payload using the NDMP operation FILE_WRITE, which is a legitimate command used by the organization to write data to a file on the server, then uses the NDMP command EXECUTE_COMMAND to execute commands on the server.
What Actions Should Businesses Take Right Now?
When dealing with a ransomware attack, having a solid backup plan is one of the most important actions any organization can take. Attackers lose their leverage if an organization can easily recover from their attacks.
We’ve seen the cyber criminal ecosystem adapt to this: In addition, many attackers will target backup resources to ensure that victims will have no choice but to pay the ransom. Establishing a recovery plan in the event of an attack, including multiple backups of organizational data, can limit the damage if your organization is targeted.
AvosLocker’s use of these vulnerabilities can also serve as a lesson in cyber crime underground operations: RaaS groups can share intelligence or steal tactics from one another in order to perpetuate their schemes. With multiple groups using Backup Exec as an entry vector, these attacks show that malicious actors do not operate in silos, and other ransomware groups may use the same vectors for their own schemes. Patching vulnerabilities as soon as possible protects organizations from all RaaS groups as they adapt to a changing ecosystem.
At-Bay is actively monitoring activity related to the Veritas Backup Exec vulnerabilities and working with affected policyholders to help them quickly mitigate risk. We urge all businesses using any of the affected Veritas Backup Exec to patch the vulnerable software immediately and follow the mitigation methods recommended by Veritas.
Even for clients who have not received a Security Alert, it’s important for them to check if they’re running vulnerable products and patch immediately.
If you have questions or other issues regarding the Veritas Backup Exec vulnerabilities, contact our Security team at security@at-bay.com.
This article is for informational purposes only. No warranty is given or liability accepted regarding this information. The provisions, exclusions, terms, or conditions of the Policy and its endorsements control in all circumstances.
Footnotes
1. SHA is the acronym for Secure Hash Algorithm, used for hashing data and certificate files. Every piece of data produces a unique hash that is thoroughly non-duplicable by any other piece of data
2. NDMP – Network Data Management Protocol, an open protocol to control data backup and recovery communications between primary and secondary storage in a heterogeneous network environment. Veritas Backup Exec server is an NDMP server